XR Background
Extended Reality (XR) is the new buzzword to describe a combination of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies. Over the years, AR/VR has evolved so much since the first head-mounted display that was built in 1960. The early advancements in this field and the early prototypes were driven by the military for training simulators. With the availability of affordable compute-intensive XR hardware and technologies, we are seeing a significant increase in the number of XR devices that can be partially attributed to the entertainment and gaming industry.
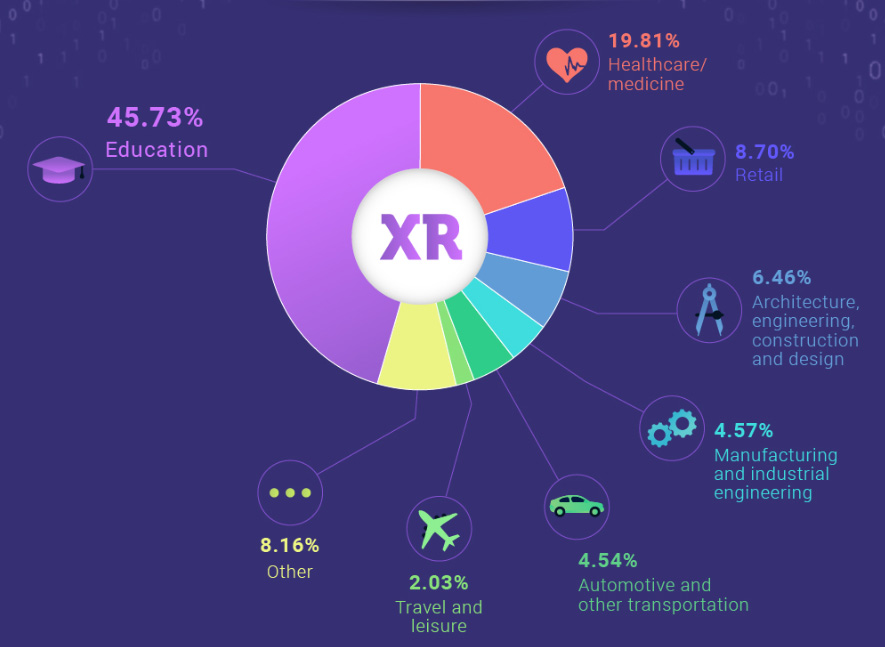
According to TechCrunch, XR is a mobile market that is gaining momentum as VR and AR markets may combine to create a $108 billion market by 2021. We are seeing the adoption of XR application for different industries including education, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and automotive.
XR Future: Convergence: one device for all functions
One of the main goals of the consumer industry is to converge devices (smartphone, VR headset, AR glasses) into one compact wearable device that is enabled with advance computing capabilities. Mobile XR has the potential to replace many devices including TV screens, gaming consoles, fitness trackers, etc. While we see few technology leaders working towards their next-gen XR devices, there are still some technical roadblocks that need to be considered.
Solving the key XR technology challenges
Display
Display is a crucial component for XR devices to ensure immersive user experience with rich visual content. Considering their portability and wearability, these displays should be light, mechanically flexible, very durable, and low cost for high volumes. XR displays have to be intelligent and capable of switching seamlessly between the real and virtual worlds.
The display has to support an appropriate Field of View (FoV) for immersive VR and useful AR. Field of view or FOV is the extent of the observable world at any specific time, and usually measure in degrees. Higher the FOV, more the extend of the virtual world. In order to support AR and VR with a single display, it has to completely support opacity for VR and yet at least have ~85% transparency for AR. For vivid experience, it should support High Dynamic Range and Wide Color Gamut.
Power and Thermal
Power optimization is very challenging for an “always-on” XR device that performs compute-intensive functionalities. At the same time, the battery has to be sleek, thin and light for the comfort of the user. Thermal management imposes stringent constraints when designing head-mounted display (HMD) devices. Thermal dissipation capacity presents unique challenges due to the limited area of the surfaces available to dissipate heat.
Connectivity
The next level of ubiquity can be ensured with high-speed wireless connectivity. The device should have extreme throughput—multi Gbps; ultra-low latency—down to 1 ms and uniform experience—even at cell edge.
Motion Tracking
XR devices need to support continuous on-device tracking for the intuitive head, hands, and eye interactions. Three Degrees Of Freedom (3DoF) refers to the tracking of rotational motion only whereas Six Degrees Of Freedom (6DoF) detects both rotational and translation head movements to help in determining the visual direction of the user. Quick detection and accurate motion tracking are important to track user interactions in real-time.
Qualcomm Snapdragon Platforms for XR Devices
Qualcomm Snapdragon 845 Mobile Platform consists of Qualcomm Adreno 630 Graphic Processing Unit to support high-end graphics, video, and display features with cutting-edge performance.
Qualcomm Snapdragon 845 platform will transform the XR landscape by providing highly immersive experiences featuring lifelike audio/visuals and intuitive interactions.
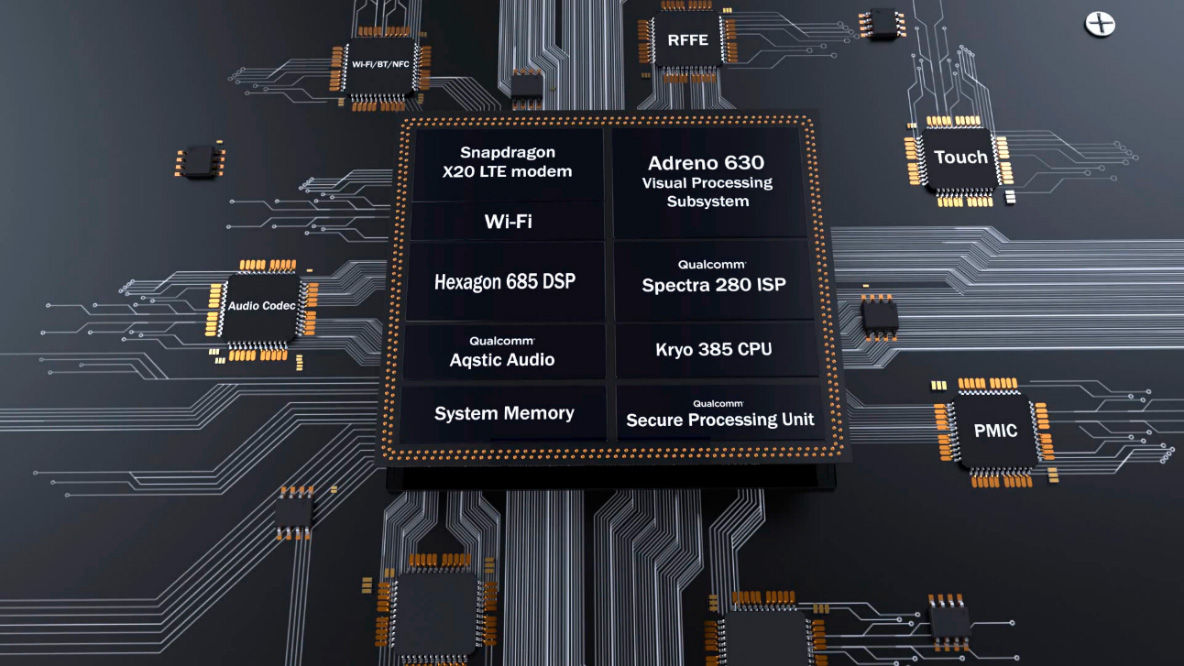
Snapdragon 845 is one of the first few platforms to support SLAM i.e. head tracking with 6DoF with simultaneous localization and mapping. This helps in devising and updating a map of the surroundings in real-time, while simultaneously keeping track of the user’s location within it.
eInfochips has strong expertise in AR/VR technologies and has enabled multiple AR/VR devices.
Case in Point
Launch of AR Smartglasses by Everysight and Qualcomm to Reshape Cycling Experience
Everysight, is a revolutionary in providing AR products and helmet-mounted displays has recently launched AR Smart glasses called Raptor. Raptor is built on the Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ 410E embedded platform using a custom board developed by eInfochips. These AR smartglasses are specially designed for cyclists and triathletes to enhance their workout and training by providing real-time information.
Leveraging experience in AR/VR technologies and being a Qualcomm Snapdragon licensee, eInfochips has developed a hardware development kit to accelerate product design on Qualcomm Snapdragon platform. Learn More







